LEER EN ESPAÑOL
In the spring of 2016, as Trump was clinching the Republican nomination for president, I drove east into the Coachella Valley, looking for a 48-year-old farmworker named Roberto. My cell phone had died and I soon became lost, meandering along country roads where I rarely passed another vehicle. When I finally found Roberto, he was standing outside a single-wide trailer, waiting patiently in his cowboy hat, with an amused smile on his face.
To the north and west of his trailer were more trailers. To the south and east his yard opened into the desert, which gave way, in places, to lettuce fields and vineyards. This was the land Roberto had worked for the past 20 years, the kind of land that made you feel small but not insignificant. We stepped inside and sat at his kitchen table. The shades were drawn against the heat, and Roberto muted the television in the living room, where a newscaster spoke in Spanish about Trump’s proposed wall along the southern U.S. border. Roberto, who wore a faded gray t-shirt and jeans torn at the knees, was built thick, with broad shoulders and the hint of a gut. He took a swig of bottled water, placed his gnarled hands on the table, and began to talk.
As he spoke, it became clear that there were plenty of reasons for him to fear a Trump presidency. He was an undocumented immigrant from Mexico, as was his wife, Leticia. (I’ve changed all the family names.) All three of their kids were born in Mexico. His youngest daughter was in eighth grade and also undocumented. His middle daughter was in college and protected by Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals, or DACA, an Obama-era policy Trump had threatened to end. Only his oldest son, married to a U.S. citizen, was a legal resident. Trump was like a grenade that could land inside the family and explode, sending people flying in all directions. Roberto rarely uttered Trump’s name, instead referring to him as the disturbio, the disturbance.
But it wasn’t only Roberto — just about everyone he knew was in a similar situation. He lives in an unincorporated community called Thermal, which, according to the U.S. Census, is 99.9 percent Latino (all but three of its 2,396 people, to be exact). In nearby Mecca, another unincorporated region of nearly 9,000, Latinos also make up 99.9 percent of the population. The community of Oasis, several miles away, is 98.2 percent Latino. Coachella, the closest city, is 97.5 percent Latino. On this side of the desert, you hear Spanish peppered with English, not the other way around.
It was my first trip to the Eastern Coachella Valley, and I was collecting the oral histories of farmworkers. During those conversations, Trump was a frequent topic. He began to feel like a specter haunting the region, his threats blasted out on the radio and television. He was also something of a joke. At the time, no one I spoke with seriously considered the idea of a Trump presidency. Then he won. The candidate who had campaigned directly against the kind of people who lived in this valley was suddenly the most powerful person in the world. I had originally come to Coachella to learn what it was like to be a farmworker here. Now there was a new question: What was it like to live in a place where everyone felt under attack?
The Coachella Valley is a 45-mile stretch of scorching terrain that begins near Palm Springs and runs southeast to the Salton Sea. It is a land of impossible extremes, a place that doesn’t make sense but exists nonetheless, a testament to hubris and hard work and irrigation canals, and also to racism. Near Palm Springs, you are surrounded by golf courses, sprawling mansions, and country clubs with swimming pools and tennis courts; as you travel southeast through the valley, they are replaced, mirage-like, by agricultural fields and dusty trailer parks. In Palm Springs you can spend $1 million renting out a lush resort for two nights. On the east side, the land is dotted with illegal dumps and the drinking water is laced with arsenic.
If you’ve heard of Coachella, it’s almost certainly because of the Coachella Valley Music and Arts Festival, an annual bacchanalia that plays out on polo grounds about 10 miles from Roberto’s trailer. The 2017 festival, headlined by Kendrick Lamar, Lady Gaga, and Radiohead, brought in a record $114.6 million. VIP tickets went for $900 apiece, and couples looking to splurge could rent a modern yurt for the weekend for $7,500. But the festival has little bearing on the lives of people on the valley’s east side, except perhaps as a reminder of how easy it is to not see them.
The region can be strikingly beautiful, with dramatic mountains to the west and date trees that march to the hazy horizon. The land is rich, producing some $640 million in crops — table grapes, lemons, bell peppers, and much more — each year.
It’s also a hard place. In Thermal, about a third of the residents live below the poverty line, including nearly half of all children. Being a farmworker isn’t easy anywhere, but here it’s particularly grueling, with summertime highs that can top 120 degrees. Housing is so tight during the grape harvest that many migrant farmworkers sleep in their cars or on flattened cardboard boxes in parking lots. Some bathe in canals polluted by pesticide runoff.
Thermal’s largest community spot lies near the intersection of 66th Avenue and Tyler Street, home to three adjacent schools in the middle of otherwise empty fields: Las Palmitas Elementary School, Toro Canyon Middle School, and Desert Mirage High School. On a cloudless morning last April, I met up with Maria, a teacher’s assistant at Las Palmitas who is a member of the Purépecha, an indigenous group from the Mexican state of Michoacán that has a sizable presence in Thermal. School had just gotten out, and we sat at a long table in an empty cafeteria, watching children race around the playground. It was Maria’s birthday — she was now 21 — and kids had spent the day serenading her with multilingual renditions of “Happy Birthday.”
- “That day they were silent. It was as if there had been a tragedy on campus. Finally, one of the students asked, ‘Are there really going to be deportations?’”
“I had my little cousin call me on election night,” Maria told me. “He said, ‘Have you voted already? I’m just really worried about my mom.’” The next day, he called in tears to ask if Maria had begun the process of fixing his mother’s immigration status so that she wouldn’t be deported, as if it were a simple matter of paperwork. “I could not respond to him,” Maria said softly. She paused, looking down at the table. “At the end, I told him, ‘Yes, I’m already doing that.’ Just to keep him calm.” She told me that her cousin was doing better now, because he thought his mother had become a legal resident. Many other parents, she said, had used the same strategy, hoping to protect their kids from worry.
On the morning after the election, students at Las Palmitas filed off the bus in a daze. Many were silent at first, but the questions eventually tumbled out. When I get home, will my mom still be there? Is the wall already built? Do they have special education classes in Mexico? Who will teach me to read? Some teachers put aside lesson plans and opened up class to a discussion about what was on everyone’s mind. “They usually come in with energy, joking around and chasing each other,” said Adam Santana, who teaches language arts at Toro Canyon. “That day they were silent. It was as if there had been a tragedy on campus. Finally, one of the students asked, ‘Are there really going to be deportations?’”
With the high school students, the fear was less on display. “The older students tend to internalize their stress a lot more,” said Karina Vega, who is one of just two full-time counselors for the almost 19,000 students in the Coachella Valley Unified School District. We met on a day when the air conditioning had gone out in her portable office, located at the district headquarters in Thermal, and her face was flushed and worried. Vega grew up in Mecca and is the daughter of farmworkers; stacked in the back of her office were boxes of dates from her father’s ranch. Her son Anzel was completing his senior year at Desert Mirage High School, which has a history of activism. In 2016, students walked out of class and marched nearly six miles to protest at the district office in support of higher salaries for their teachers. A couple of years before that, they marched out after the principal and vice principal were fired. “Our kids have hearts, big hearts,” Vega told me.

Image: Kate Gavino/Longreads
In some schools across the country, Trump inspired white kids to chant, “Build the wall!” at their Latino peers. That sort of thing wouldn’t happen here, because there aren’t any white kids. Santana, the middle school teacher, tries to prepare his kids for encounters like that in the world outside Thermal. “I tell them, when you go off to college, or if you move and get a job somewhere else, it’s going to be very different. Not everybody is going to have similar last names as you, or the same hair color. They’re not all going to speak Spanish.” The isolation has become a source of strength and comfort. One high school senior, a DACA recipient, told me that he first lived in Bloomington, in San Bernardino County, and was beaten and bullied by kids because he was still learning English. “We moved here when I was in second grade, and I would want to speak Spanish and English, and everyone was able to talk both. I was like, ‘Oh, so this is where I belong.’ They understand me and my struggles, and I understand them.”
Since the election, Vega has dealt with a surge of self-destructive behavior among the high school students. “With grief, we can figure it out,” she told me. “If someone dies, I know what to do with that.” But the general climate of fear, the threats of family separation, the fact that no one knows what’s coming next — these were existential problems that she told me “couldn’t be counseled.” She had recently attended a training that featured a speaker who described, during a particularly rough stretch of her life, drinking hot sauce. “When she would feel the fire going down her throat, she would be like, ‘Oh, there I am,’’ Vega said. “I feel like that’s where we are right now as a community. We need to feel. And I’m not saying that all of this wasn’t real under Obama, but now it’s a constant. It’s all you hear, it’s all they talk about.”
Undocumented immigrants were far from safe under Obama. During his administration, a record 2.8 million people were deported. He also oversaw the dramatic expansion of a program called Secure Communities, which allowed for information sharing between the Department of Homeland Security and local law enforcement agencies and led to the deportation of many individuals with infractions as minor as driving with a broken taillight. It was only during his final years in office, under pressure from activists, that Obama became less hawkish on immigration, creating the DACA program to protect young undocumented immigrants, and trying, unsuccessfully, to expand those protections to their parents. His legacy was, at best, mixed.
There was nothing mixed about Trump. During the campaign, Trump’s slander against Mexicans was repeated incessantly on Spanish-language news programs, sucking up the oxygen in living rooms across the Coachella Valley like a loud and unruly family member. Then he won and his threats started to mean something. In his first month in office, Trump signed an executive order that abandoned Obama’s tiered system, essentially making any undocumented immigrant a priority for deportation. That was followed by several weeks of stories about immigrants being swept up across the country, including 161 in the Los Angeles area. Similar actions had been carried out under Obama, but now they felt like the opening shot in a war. Under Trump, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents were given new powers to pick up anyone they encountered, in what the agency termed “collateral arrests,” and apprehensions in the first year jumped 40 percent. Agents arrested defendants inside courthouses, homeless people seeking shelter at a church, and even a 23-year-old protected by DACA. “The crackdown on illegal criminals is merely the keeping of my campaign promise,” Trump tweeted on February 12, 2017. Here in Coachella, which is also home to a Border Patrol station, the message was clear: No one was safe.
Berta, who lives down the road from Roberto, was the first person to tell me about the raids in the Coachella Valley. (I’ve changed her name.) On February 15, 2017, she was home at work as a nanny, watching two young children when she got a call around 10 a.m. It was a friend, who heard from a neighbor that Border Patrol vans were parked in front of the local Cardenas, a grocery store chain that caters to Latinos. Then her brother-in-law called; he’d read a post on Facebook that raids were underway. Over the next hour, the calls kept coming — Berta lost count after 10 — and the scope of the operation expanded. Immigrants were being rounded up at Cardenas stores in two nearby cities, Cathedral City and Coachella, and at a Walmart and a Food 4 Less. Agents were demanding documents from anyone entering or leaving. Some attempted to flee, leaving behind carts filled with food. Others sheltered in place, refusing to exit. On the streets, Border Patrol agents set up checkpoints, sweeping up drivers who couldn’t prove their legal status. News of the raids soon leaped from social media to a local Spanish-language radio station.
- “What would happen if they got my husband? Or if they got me? What would happen to my kids?”
As the calls kept coming, Berta veered into something close to a breakdown. Her husband, also undocumented, works in demolition and travels to construction sites across the Coachella Valley. When she reached him, he was at a jobsite not far from Cathedral City. He had already received numerous warning messages on Facebook.
Berta paced her small trailer, exchanging texts, shooting off Facebook messages, absorbing the panic and sending it back out. Her husband was 30 miles away; one wrong turn and he’d be sent back to Mexico. Finally, Berta called her sister-in-law, a U.S. citizen. Like everyone else, she had heard about the raids, and she volunteered to drive through the streets where Border Patrol checkpoints had reportedly been set up.
Berta’s sister-in-law drove for more than an hour and didn’t come across a single checkpoint. There were no agents at Cardenas, or Walmart, or Food 4 Less. There were, in fact, no raids or checkpoints in the Coachella Valley that day. When Berta got the news, she broke into tears of relief.
It was mid-April when we spoke, two months after the false rumors had terrorized the valley. As Berta described that day, her hands shook and she began to cry all over again. “I decided not to worry anymore,” she said, wiping her eyes. “It’s too stressful to think about all the possibilities.” She paused and thought about the possibilities. “What would happen if they got my husband?” she asked. “Or if they got me? What would happen to my kids?” Their oldest son, at 18, had just renewed his DACA permit; their youngest son, then 14, was too young to enroll.
Berta had just heard on the news that Trump’s new priority was to deport people who had overstayed their visas. Berta had overstayed her visa, and the government had the address of her brother-in-law, whom she had said they were visiting. “That’s the first place they’re going to look for us,” she said. She looked at her watch. It was 3:30 in the afternoon. We were seated in her trailer with the curtains pulled shut. Her husband wasn’t due to be home for several hours, but she was already beginning to worry.
Thermal’s Migrant and Seasonal Head Start center is located in a yellow one-story building across the street from Vega’s office. When I visited, several months after Trump took office, I met the director, Beatriz Machiche, a former farmworker. Down the hallway was an empty classroom with a sheet of paper taped to the door that read, Cerrado hasta nuevo aviso, Jan 2017. They had closed the classroom because they didn’t have enough kids. This time last year, they had a waiting list 200 kids long. Machiche told me she suspected parents no longer wanted to turn over their information to the federal government for fear of being deported. She and her staff had started making trips to the fields to spread the word about their services, but so far, people were reluctant. “Parents say they will come, but they don’t,” she said. In more than a decade at the office, she’d never seen anything like it.
This was one of the harshest consequences of the fear: Immigrants were staying away from the very institutions designed to sustain them and elevate their children. In California, several other agencies that provide Migrant and Seasonal Head Start care reported drops in enrollment last year of between 15 and 20 percent. One of the largest Migrant and Seasonal Head Start grantees in the country is the Texas Migrant Council, which operates in seven states; last year, the number of kids they served dropped 11 percent. In Texas, the number of students assisted through the federally funded Migrant Education Program, which provides assistance to children of migrant farmworkers who face special obstacles accessing education, dropped 22 percent from 2016 to 2017. In California, the drop was 7 percent.
The fear was also causing people to go hungry. After the false Cardenas rumors, Veronica Garcia, who works with Borrego Health, a nonprofit health care provider, was knocking on doors at a trailer park in Thermal. A woman in her 60s told Garcia that many of her neighbors had stopped shopping, convinced that immigration agents were staking out grocery stores. As their cabinets emptied out, she had begun to travel to local distribution sites to collect free food that she’d pass out to grateful families. As she spoke to Garcia, hungry kids walked by her home to pick up peanut butter sandwiches. By the end of the conversation, tears were streaming down the woman’s face.
“She was letting us know how bad it had gotten for everybody there,” said Garcia. “People were too scared to come out at all.” Garcia had previously worked at Coachella Valley’s food bank, Food in Need of Distribution, or FIND. She contacted them and explained the gravity of the situation, and several hours later a truck rolled into the trailer park. Within hours, nearly 200 people had been fed.
Chantel Schuering is the community relations director for FIND, and says that they typically sign up about 3,000 families a year for Medicaid and food stamps. After the election, their numbers dropped by more than half, a trend that lasted into the spring. Across the country, programs that feed the hungry have seen sharp drops in enrollment. In California, the number of participants in the Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children, or WIC, dropped 7 percent last year. In Florida, the decrease was even higher, at 9.6 percent. Texas participants were down 7.4 percent.
Many people I interviewed emphasized that they couldn’t definitively explain the drops in enrollment, but they believed that fear of deportation was a contributing factor. Sometimes, though, the link was direct. After a raid in February 2017 in Woodburn, Oregon, during which ICE picked up two vans of farmworkers, several local families responded by calling the Oregon Child Development Coalition, which provides Migrant and Seasonal Head Start services for the state, to demand that their names be expunged from the database. In Coachella, FIND received numerous calls from residents wanting to learn how to unenroll from food stamps and Medicaid. This February, those fears received confirmation: Reuters reported that the Trump administration was working on new rules to punish immigrants for enrolling their U.S.-born children in Head Start, food stamps, and other programs.
- “People [once] felt pretty safe here. In the new political climate, it’s like they’re going to go after everyone.”
The fear also appears to be causing immigrants to hesitate before they report crimes. Last April, Houston’s police chief announced that the number of Hispanics who reported rape had dropped nearly 43 percent in the first three months, compared to the same period the previous year. During the first sixth months of the Trump administration, domestic violence reports among Latinos dropped 18 percent in San Francisco, 13 percent in San Diego, and 3.5 percent in Los Angeles. (There was virtually no change in reporting among non-Latinos.) Sarah Stillman, writing in the New Yorker, reported that in one Latino neighborhood in Arlington, Virginia, domestic violence reports dropped more than 85 percent in the first eight months of 2017, compared to the previous year, while rape and sexual complaints were down 75 percent.
In the months after the election, people in Coachella altered their daily routines, recalculating risks. Attendance at the largest Catholic Church in the Coachella Valley, Our Lady of Soledad, dipped between 10 to 15 percent. “People [once] felt pretty safe here,” said Father Guy Wilson. “In the new political climate, it’s like they’re going to go after everyone.”
Another woman told me that her husband, an undocumented immigrant, had stopped wearing political T-shirts, which amounted to a subtle erasing of his personality. Others eliminated trips to the movies or to local restaurants, because each journey increased the chance of being stopped by Border Patrol. One afternoon, I rode in the car with an undocumented woman who was picking up her son from a community college class. During the drive she gripped the steering wheel and repeatedly scanned her mirrors for the green-and-white truck of an agent. When we got back to her trailer we both collapsed on the sofa, relieved. This did not feel like a sustainable way to live.
Last April, the Desert Sun, the local newspaper, reported that medical clinics were seeing drops in the number of patient visits. Doug Morin directs Coachella Valley Volunteers in Medicine, a free clinic that serves individuals without health insurance, filling a gap in a region where the doctor-to-population ratio is more than four times federal recommendations. The clinic once did a brisk business. “Every month and every year, our numbers went up,” Morin told me. In January, when Trump took office, patient visits nose-dived. They had 171 patient visits that month, down from 429 in January of 2016. When we spoke in September, he said visits were down by 25 to 30 percent for the year.
Morin told me of one elderly woman who had come to the office complaining of abdominal pain. She had previously gone to the emergency room of a local hospital, where doctors discovered a mass on her uterus, but because she didn’t have insurance, she was sent on her way. At Morin’s clinic, a physician determined that the mass wasn’t fibroids, a common and treatable condition, but likely a cancerous tumor. As a staff member filled out paperwork to enroll the woman in Emergency Medi-Cal, which is available to undocumented immigrants, the woman’s daughter entered the office.
“She told us, ‘Delete everything!’” said Morin. “She didn’t want her mother’s name or address to be shared with anyone.” They tried to explain the severity of the condition, but the daughter grabbed the paperwork and marched her mother out. “She left so quickly that we weren’t even able to give her mother anything for her pain,” recalled Morin.
Last year, as winter turned to spring, I stopped by Roberto’s trailer several times and always found him defiant and unafraid. More rumors of raids had swept through the valley, and Roberto’s supervisors had recommended that employees travel in small groups to avoid attracting attention from immigration officials. Roberto saw Border Patrol agents just about every day, sometimes idling behind his car at a red light, other times in line when getting coffee at a nearby market. When I asked him how he felt when he saw a Border Patrol truck in the rear mirror, he shrugged. They were doing their jobs and he was doing his.
He told me that he had lost his fear a decade ago, when his son, Angel, had nearly died. At the time, Angel was 16 and picking grapes near Bakersfield with him. The temperature hit 104 degrees, and Angel began to complain that he felt dizzy and too weak to work. After Roberto insisted that his son be taken to the hospital, the company put Angel in a truck, placed ice bags under his armpits, and brought him to a clinic.
Angel was dropped off at home that evening looking pale and weak. He couldn’t tell his father what kind of treatment — if any — he had received. He spent the night sweating and vomiting in the 14-foot-by-14-foot room that their family of five then shared in their employer’s primitive labor camp. It was only after an organizer with the United Farm Workers drove Angel to the hospital that doctors finally diagnosed him with sunstroke and discovered that he’d been exposed to the West Nile virus. The sunstroke weakened his immune system, likely causing the West Nile to develop into meningitis, an infection that inflames the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Angel went into a coma, and for a time it seemed he might not survive. When he regained consciousness, Roberto greeted his son in the hospital room. Then he stepped into the hallway and kneeled on the ground, overcome.
“That takes your fear away,” he told me. “What can anyone do to me now?” Before, he had been a hard but quiet worker. After Angel’s brush with death, Roberto traveled to Sacramento to share his story and speak out in support of heat protections for farmworkers, which were signed into law in 2005 by then Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger. Roberto now stood up to supervisors who disrespected workers; he had also begun to take his phone into the fields, where he videotaped farmworkers speaking about their lives. His oldest daughter, Rosa, was majoring in journalism, and Roberto had become something of a farmworker-journalist himself, uploading the videos he took to Facebook. In one, he addressed Trump directly. “These are the people that the politicians don’t want, but while they sleep at this hour, all these people are working in the fields across California,” he said, as a crew harvested celery stalks in the background. “And a greeting to Donald Trump, who doesn’t want us. I invite him to come here and find out about our work. This here is celery, which gives flavor to this soup.”

Image: Kate Gavino/Longreads
It wasn’t hard to find fear in the Coachella Valley, but there was resistance as well. One evening, I visited Jorge Ortiz at his house in Coachella, where he lives with his wife, Ymelda, and their three sons. Their living room was filled with unpacked boxes — they had recently moved — and Ortiz sat on the couch, hunched over and exhausted. The 44-year-old had just arrived home from a long shift as a foreman at a landscaping company. He worked weekends as a caterer, and sometimes picked up the odd gardening or construction job. “I have the same story as everyone else: I was going to stay here two or three years and go back to Mexico,” he told me. That was 17 years ago. When he started to rise at the landscaping company, he sent for his wife and kids instead. Their two oldest kids have DACA, while their third son is a U.S. citizen. Jorge and Ymelda remain undocumented.
- “I would like to send a message to my Latino people: show your faces,” he told the camera.
Because he refuses to hide his identity when giving media interviews, Ortiz has become one of the most recognizable immigrant activists in the area. One of his landscaping clients is a veterinarian who cares for dogs used by the Border Patrol; Ortiz greets the agents when they arrive. Last year, on May 1, he joined fellow activists at a protest in front of the local Border Patrol station. Just a week earlier, Ortiz and his family had been profiled in a widely watched video made by AJ+ that showcased his activism. “I would like to send a message to my Latino people: show your faces,” he told the camera. It was a stance that made the people around him nervous. At the May protest, another participant insisted Ortiz don a black hat and sunglasses to conceal his face; another walked alongside him to guard against any attempt by border agents to seize him.
Ortiz, I think, could sense that I was struggling to understand his lack of fear. He told me that he had got his start as an activist a decade ago with a group called the Council of Mexican Federations, or COFEM, which helped parents become leaders within Coachella schools. As he became more vocal, other undocumented immigrants starting calling him to ask for his advice, or simply to worry aloud about the future. Since Trump’s election, the calls had skyrocketed, and he had seen how fear could grow until the life you were living didn’t look much like a life at all.
Ortiz admitted that he did, of course, have fear. He didn’t want to be separated from his family, and he wanted his sons to be able to continue their studies in the United States. But he didn’t want to be ruled by fear. So his answer was to push the fear aside and charge forward. “If you call for fear, fear will come,” he told me. “But if you call for faith, faith will also come.”
On a Saturday in June, I pulled into the driveway of Roberto’s trailer. It was a few minutes past noon and the temperature was on its way to 106. Roberto was outside, in the shade of a carport he had recently built, next to a fence he had recently completed, adjacent to a shed he had cleaned out and converted into a small music studio. He liked to come home from a day in the fields and tinker around out back, as if he’d spent the shift bottled up in an air-conditioned office.
Today, though, he wasn’t working. An accordion was slung over his shoulders and he was squeezing out a melody. Several large jalapeño peppers rested on a nearby folding table, which he had risen before the sun to pick. Roberto often had a playful sparkle in his eye, but now he was positively beaming.
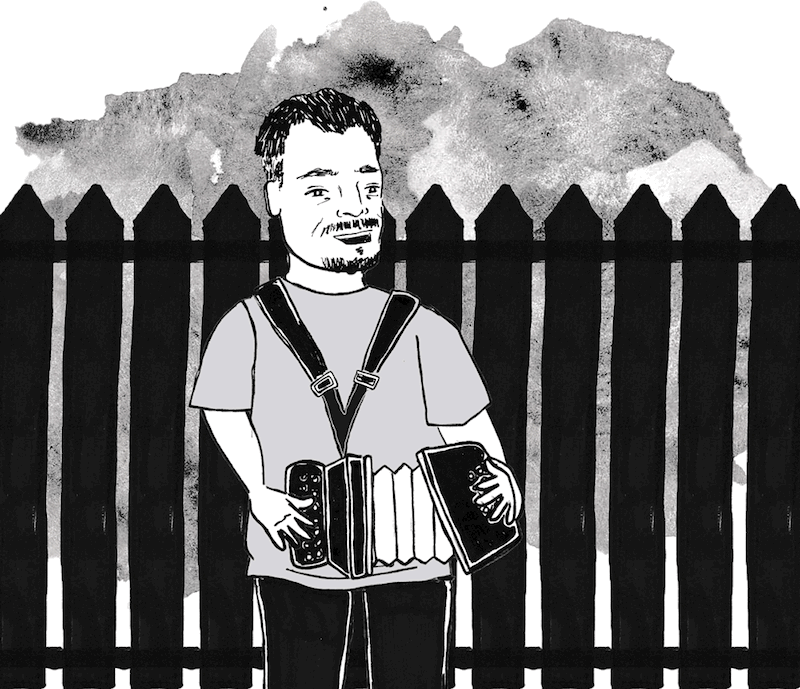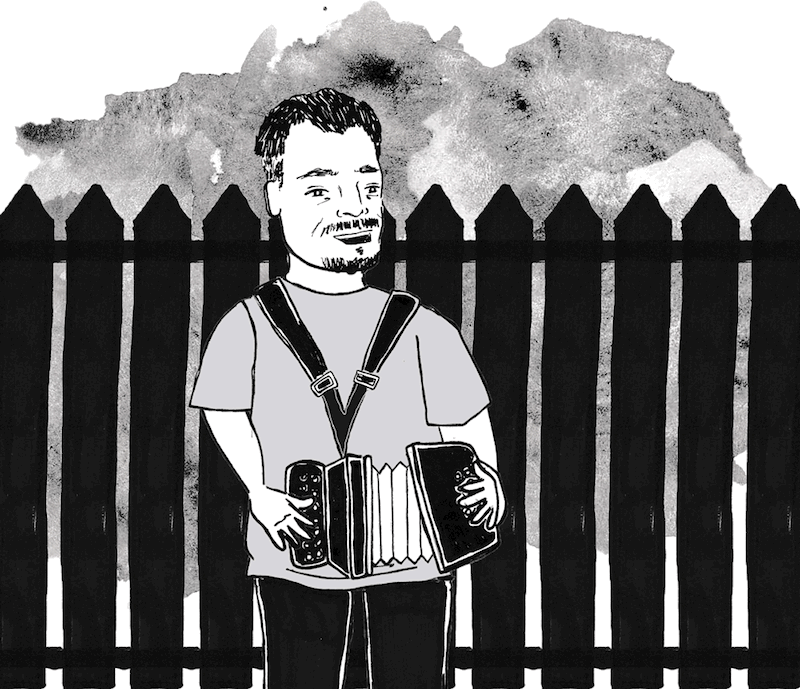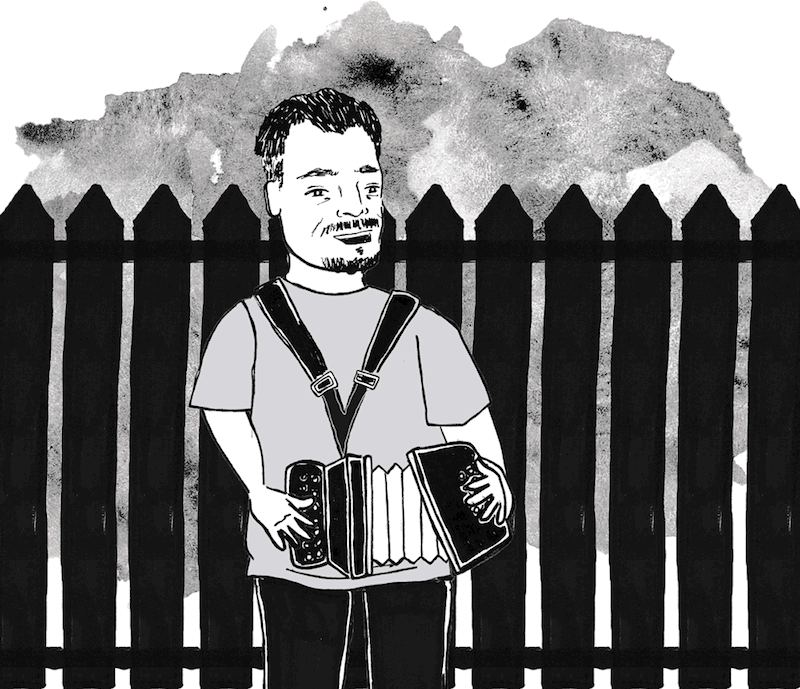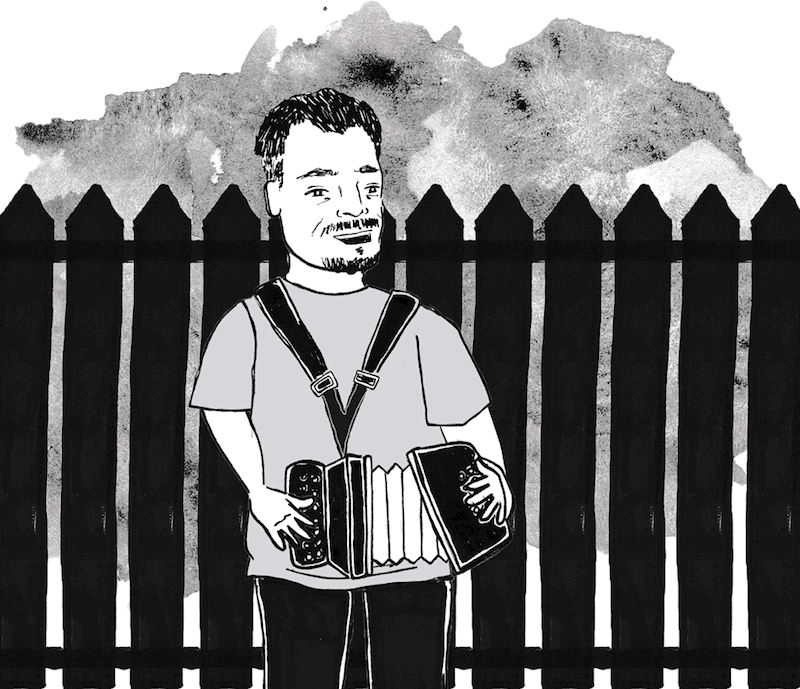
Image: Kate Gavino/Longreads
“Rosa graduates from college today,” he said. He put the accordion down, pulled up a stool, and offered me a chair. He would need to clean up soon and head into Los Angeles, but right now he was luxuriating in the moment. Rosa was why they had landed in the United States in the first place. Back in Mexicali, Roberto worked at a bread company called Bimbo, where he monitored a toasting line. When he asked to have a day off for Rosa’s baptism, his supervisor denied the request. Roberto, who had never missed a day of work, went anyway. How could he miss the baptism of his own daughter? For that, the supervisor suspended him for 15 days. Furious, Roberto walked out and never came back.
After that, he hadn’t found steady work, so the family came to the United States on a tourist visa and never went back. As a slight breeze tickled the sweat on my neck — Roberto didn’t sweat, as far as I could tell — he talked about Rosa’s future. He knew that she was a hard worker and had dreams of being a journalist, but he wasn’t sure of her plans after graduation. She moved in a different world already and was rising and happy. That was all he needed to know. “I told her, just because we helped you out, you don’t owe us anything,” he said. “You make your own path and don’t worry about us.”
After half an hour, I left Roberto so that he could go inside and shower. He had picked out a sparkling outfit for the big day: a sleek purple and blue dress shirt, black slacks, white cowboy boots and a matching white tejana, or cowboy hat. Despite the disturbio, his family was moving forward.
Jose Simo is a soft-spoken counselor at the College of the Desert, a community college in the Coachella Valley that serves as many young people’s path out of the fields. In 2008, he founded Alas Con Futuro, or Wings to the Future, a club to support undocumented students and connect them with scholarships and financial aid. On September 5, the club held its first meeting of the 2017-18 academic year, where they planned to introduce the group to new students. Several hours before they met, Trump announced that he was canceling DACA, and Simo’s phone started buzzing with texts. The meeting turned into a confessional, with students going around the table, sharing their fears, wiping away tears. “People were just devastated,” said Simo. “It was incredibly difficult. Yet I’m always amazed at how resilient the students are. The fifth of September was hard, and the sixth was hard, but by the seventh, they were just going to move forward.”
Several weeks later, Simo was in a meeting room at the college, where two-dozen people had gathered for a DACA clinic. At the front of the room stood Luz Gallegos with a group called TODEC Legal Center. She began the workshop with a story about her first activist campaign, in 1986. Gallegos, at age 7, traveled with her parents to Washington, D.C., to lobby members of Congress on immigration reform. While they had raised enough money for their airfare, they couldn’t afford lodging, so they spent their week in Washington sleeping under a bridge. Each morning they’d clean up at a local church and descend on the Capitol.
Her point was that victory was possible: President Ronald Reagan, a conservative Republican, had signed an immigration reform bill that legalized the status of nearly three million undocumented immigrants. I’d seen Gallegos in action before, and this was always her message: You could win if you fought. “You are not alone,” she told the students. “You don’t need to have fear, because that’s what they want you to feel. There are so many people behind you, supporting you. Don’t forget that you are the very best of the best, the crème de la crème.”

Image: Kate Gavino/Longreads
Trump had announced March 5, 2018, as the official end date for DACA, though recipients whose protections expired before then could apply for another two-year reprieve. The deadline to send in renewals was October 5, and Gallegos was scrambling to reach as many people as she could, giving upward of three workshops a day. She’d once told me that after the election her organization had instituted a policy of self-care to prevent burnout and help staff manage the emotional stress that came with working with a community in crisis. That was five months ago, and she didn’t look like she had taken many days off since. When I asked her about it, she just laughed. Time for rest would come later. She excused herself to help a DACA student fill out her paperwork.
When I swung by Roberto’s trailer, he was uncharacteristically quiet. “Do you think we made a mistake with Dolores?” he asked. In July, his youngest daughter had turned 15, which meant she was eligible to apply for DACA, but Roberto had been hesitant to turn over any more information to the federal government as long as Trump was president. Now even that limited protection was gone. And what about Rosa, whose life after college was just starting to unfold?
- Those were all sacrifices made for the benefit of his kids. Could everything really be wiped away in an instant?
“We work, and maybe from the viewpoint of others we look happy,” he said. “But we are uncertain.” He was seated on the couch next to Leticia, who remained quiet throughout, as she often did. The couple looked exhausted. The season had shifted again, and they were now planting celery for $10.50 an hour, a task performed at night to protect the young seedlings from the daytime heat. “We don’t know what will happen tomorrow,” he said, his eyes turned to a soap opera on the television. “Sometimes we get off work at two or three in the morning and we could just be pulled over by immigration and that’s it.” For the first time, he hinted at the prospect of defeat. He spoke of getting older without any retirement savings, of a life without unemployment insurance or health care, of his parents in Mexico, who had both died without him being able to say a proper goodbye. Those were all sacrifices made for the benefit of his kids. Could everything really be wiped away in an instant?
Dolores hadn’t been around during earlier visits, but today she was home and came out of her room to chat. The high school sophomore has long black hair with bangs cut short across her forehead, framing a broad face and bright smile. She was 2 when the family moved to the United States, and except for trips to Bakersfield during the grape harvest, she’s spent her entire life in the trailer park. She told me that her playground was the surrounding desert, where she invented characters and talked to the palm trees. “I would make believe that I was a knight and I would be trying to save princesses,” she said with a laugh. “I’m pretty sure my parents thought I had a screw loose.”
Dolores seemed to be taking the news of DACA’s cancellation better than her father. At times she felt lost, and she worried about her sister Rosa, who was her best friend and mentor. Dolores had always dreamed of studying abroad, which now seemed impossible. But she still had the same goal in sight: to attend the University of California at Berkeley. “If I have to work twice as hard, three times as hard, there’s no doubt in my mind that I’m going to do it,” she said. “My sister tells me, ‘It’s not hard — it’s time consuming.’” The phrase has become something of a mantra for Dolores, who studies up to five hours a day, writing by hand because the family doesn’t own a computer. Her current class schedule includes AP world history, AP multicultural literature, AP Spanish, math honors, physics, and dance. “You try to get as many AP and honors classes as you can, ’cause they’re going to help you out,” she said, saying she was frustrated Desert Mirage didn’t offer more advanced courses than it did. She’s only ever received A’s.
Dolores told me that she wanted to be the first person in her family to graduate in a white gown, an honor reserved for the 10 best students in the school. She doesn’t yet know what she wants to study. What she knows is that she never wants to step foot in the fields, and that with a good job she can help support her parents. “They work extra hours and are paid so little,” she said. “I know they’re being yelled at. I remember my dad with all of his hands bruised and my mom’s knees aching. They come home so tired.” Behind Dolores, Roberto had fallen asleep on the couch and was snoring gently.
When I last visited Roberto, it was dusk on the day after Thanksgiving and the sky over Coachella had turned a gorgeous purple. Rosa was visiting from Bakersfield, where she had gotten a job advocating for immigrants, and we stood outside the trailer, enjoying the evening breeze as she described her work. She attended protests and wrote articles and would soon be traveling to Washington, D.C., in support of the Dream Act, which, if passed, would provide a path to citizenship for undocumented youth. Roberto stood next to her, smiling.
In the Coachella Valley, fear appeared to be in a moment of retreat. After rumors of raids and massive deportation forces, many people told me that things had entered a period of normalcy. Doug Morin, of Coachella Valley Volunteers in Medicine, said patient visits had rebounded. Enrollment at Migrant and Seasonal Head Start had also bounced back, thanks in part to the aggressive outreach of Beatriz Machiche and her staff. It wasn’t hard, though, to imagine how quickly everything could change. In the first few weeks of 2018, there was a visible increase in Border Patrol agents throughout the Coachella Valley, which led to fresh worries of an enforcement action (though, again, none materialized). In February, as part of a national crackdown on employers, ICE agents visited several local businesses to conduct audits. At one restaurant, a number of customers abruptly left after the ICE agents entered, only returning later in the afternoon to pay their bills. For undocumented families, fear can surface at a moment’s notice.
Shortly after Valentine’s Day, Roberto called with good news: Dolores was ranked eighth in her sophomore class of 516 students, which meant she was on track to graduate wearing white. She had also recently asked her parents to organize a fiesta dequinceañera, the coming-of-age celebration for girls when they turn 15. Dolores had turned 15 last July, but the summer had passed without a party because money had been tight. Money was still tight, of course. But Roberto told me “she has never asked for anything,” and so he and Leticia promised their daughter a big party, setting a date for May. They needed to hire musicians and a videographer, feed everyone, and rent out a space. Roberto estimated it would cost $7,000 to pull it off. He didn’t know where they’d get that kind of money, but he had no doubt that they would. He was nearly 50 years old, but he was a dreamer, too.
This article was reported in partnership with The Investigative Fund at The Nation Institute, with support from the Puffin Foundation.